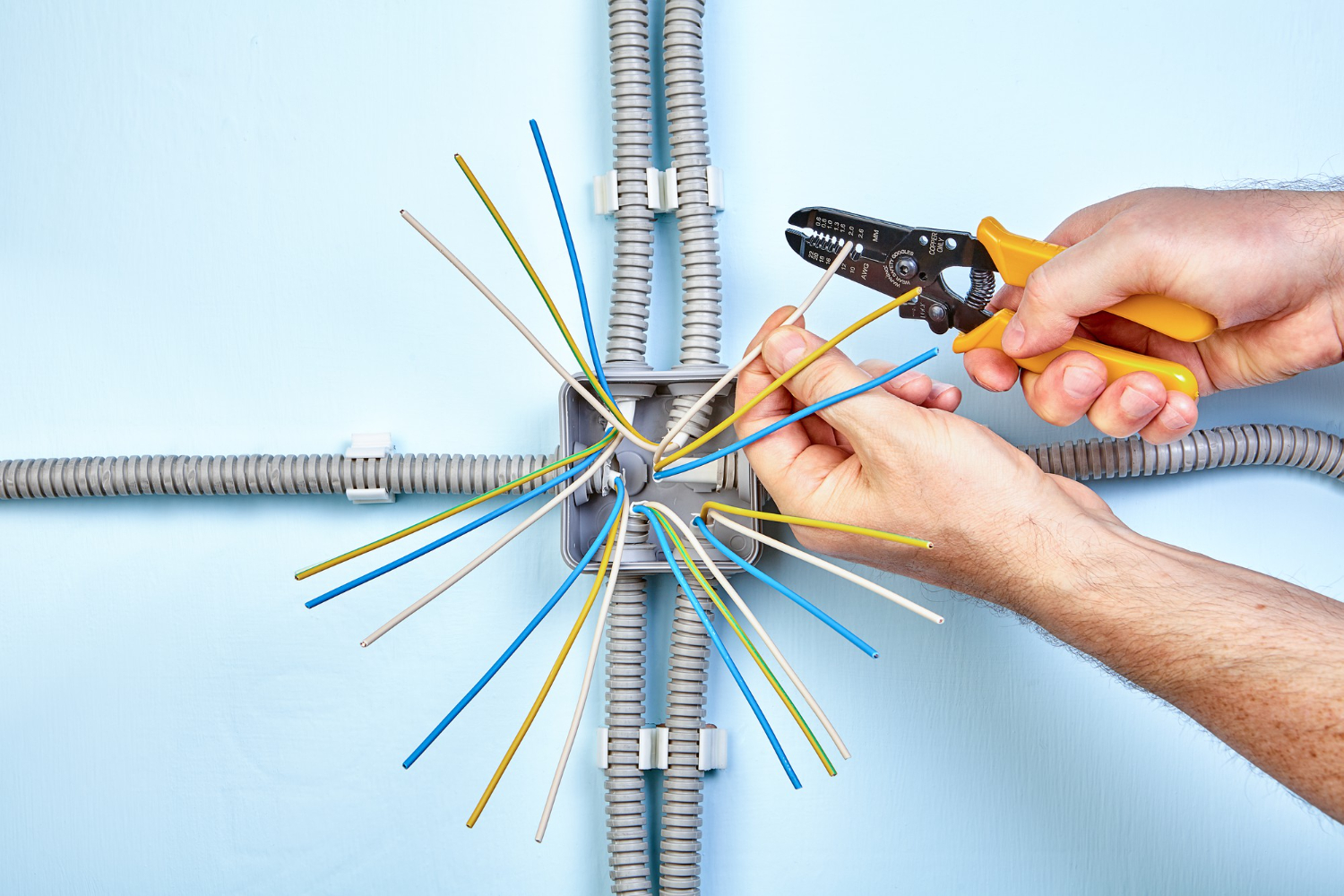
Installing electrical wiring requires precision, compliance with safety guidelines, and a clear understanding of the materials involved.
One common question for any DIYer or electrician is whether a 10/3 wire cable can be installed in conduit. The short answer? Yes, you can—but as with most electrical installations, there are rules, guidelines, and best practices to follow.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about installing 10/3 wire cable in conduit, the benefits, challenges, and practical steps to help you tackle the task safely and effectively.
What is 10/3 Wire Cable?
To start, it’s important to understand the components of 10/3 wire cable. The “10” indicates the wire’s gauge, meaning it’s 10-gauge, and the “/3” refers to three insulated conductors inside the sheathing, along with a bare or green ground wire.
Common Uses of 10/3 Wire
10/3 wire cable is typically used in residential or light commercial wiring for high-demand appliances such as:
- Electric dryers
- Water heaters
- Air conditioners
- Kitchen ovens and ranges
Its ability to handle up to 30 amps makes it a reliable choice for powering heavy-duty appliances.
Can You Install 10/3 Wire Cable in Conduit?
Yes, you can install 10/3 wire cable in conduit, but there are specific considerations and code regulations to keep in mind. The National Electrical Code (NEC) allows nonmetallic sheathed cable (NM-B, commonly called Romex), which includes 10/3 wire, to be run through conduit when additional protection is needed.
Scenarios Where Conduit is Advisable (or Required)
Installing 10/3 wire in conduit can be helpful or required in situations like:
- Protection from Physical Damage: Areas prone to impact or environmental hazards (e.g., garages or basements).
- Outdoor Runs: Protecting the wiring from exposure to moisture or sunlight.
- Code Compliance: Certain local codes may require conduit in specific applications regardless of the setting.
However, keep in mind that running 10/3 cable through conduit is often more cumbersome than using individual wires like THHN due to its large size and stiffness.
Benefits of Using Conduit with 10/3 Wire Cable
- Enhanced Protection
Installing conduit safeguards the wiring from physical damage, moisture, corrosive elements, and more.
- Improved Safety
Conduit reduces the risk of punctures, abrasions, or electrical shorts, ensuring a safer environment.
- Code Compliance
Utilizing conduit can help meet local building codes in scenarios where wiring is exposed or requires additional support.
- Longevity
By encasing 10/3 wire in conduit, you extend its lifespan by shielding it from wear and tear.
Challenges of Installing 10/3 Wire in Conduit
While there are benefits, challenges can arise due to its size and stiffness.
Fit and Flexibility
- 10/3 wire can be difficult to pull through narrow conduits, especially if the run includes bends.
- Using an undersized conduit can cause overheating, wire damage, or installation failures.
Conduit Sizing Requirements
- Calculating and choosing the proper conduit size is critical to ensure a smooth installation. The NEC specifies that conduit fill percentage must not exceed 53% for a single wire.
For 10/3 wire, a conduit size of ¾-inch or larger is typically recommended depending on the wire distance and bends in the run.
How to Install 10/3 Wire in Conduit
Follow these steps to ensure a safe and effective installation:
Step 1: Check Local Electrical Codes
Start by reviewing the NEC guidelines and any local building code amendments. Your installation must always comply with safety regulations, particularly regarding conduit size, cable type, and suitable environments.
Step 2: Choose the Right Conduit Type
The type of conduit significantly impacts the installation. Common options include:
- PVC Conduit: Lightweight, ideal for outdoor use.
- EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing): Rigid but thinner-walled, perfect for indoor runs.
- Flexible Conduit: Suitable for installations requiring bends or curves.
Always choose a material that suits the intended environment and safety requirements.
Step 3: Select the Proper Conduit Size
The diameter of the conduit is key to avoiding overcrowding. Use the NEC’s Chapter 9 tables for conduit fill:
- For a single 10/3 wire cable, ¾-inch conduit is a good starting point.
- Upgrade to 1-inch conduit for longer runs with multiple bends to ensure easier pulling.
Step 4: Prepare the Wire
- Use a wire lubricant to reduce friction during the pulling process.
- Inspect wire insulation for any damage before installation.
Step 5: Pull the Wire Through the Conduit
- Use a fish tape or pull string for longer runs.
- For straight runs, gently guide the wire through the conduit by hand. For more complex routes with bends, consider using pull boxes midway through the run.
Step 6: Secure and Test
- Anchor the conduit to walls, ceilings, or other surfaces using approved clamps.
- Once installed, test the wire for electrical continuity and verify compliance with the NEC requirements.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using the Wrong Conduit Size
Undersized conduits can cause installation difficulties and lead to overheating risks.
- Skipping Lubrication
Longer runs without lubrication increase friction and can damage the wire sheathing.
- Improper Anchoring
Ensure the conduit is securely fastened to prevent wear and tear over time.
- Exceeding Fill Capacity
Installing too many wires in a single conduit can increase heat build-up and compromise safety.
Practical Applications of 10/3 Wire in Conduit
Here are some scenarios where 10/3 wire in conduit is ideal:
- Garage Wiring
Protects cable run along walls against potential damage from tools or vehicles.
- Outdoor Installations
Conduit shields 10/3 wire from sunlight exposure or moisture in patios and garden sheds.
- Basements
Keeps wiring safe in high-traffic areas prone to bumps or scrapes.
For example, wiring a dryer circuit in a detached garage often involves running 10/3 wire through conduit to ensure safety and compliance.
Ensure Safe and Effective Electrical Wiring
Installing 10/3 wire in conduit is a practical way to protect your electrical system, comply with local codes, and enhance safety. By following the guidelines and tips mentioned above, you’ll achieve a secure and efficient installation.
When in doubt, consult a licensed electrician to ensure your project meets industry standards and safety protocols. A little extra effort now can save you from major headaches (and hazards) down the road.
FAQs
What Size Conduit Do You Need for 10-Gauge Wire?
For 10/3 wire, start with a ¾-inch conduit for standard runs. Larger sizes (like 1-inch) may be necessary for longer or more complex installations.
Is it Legal to Run Romex in Conduit?
Yes, NM-B (Romex) can be installed in conduit when additional protection is necessary. However, it’s not ideal for long, complex runs due to its stiffness.
What Type of Cable Can Be Run in Conduit?
You can use NM-B, THHN, or UF-B wires in conduit. For wet locations, THHN or UF-B wires are recommended due to moisture resistance.
How Many 10-Gauge Wires Can Fit in ¾-Inch Pipe?
Typically, a ¾-inch conduit can accommodate one 10/3 cable. Larger configurations may require wider pipes to comply with NEC fill requirements.